What is the most effective natural sleep aid?

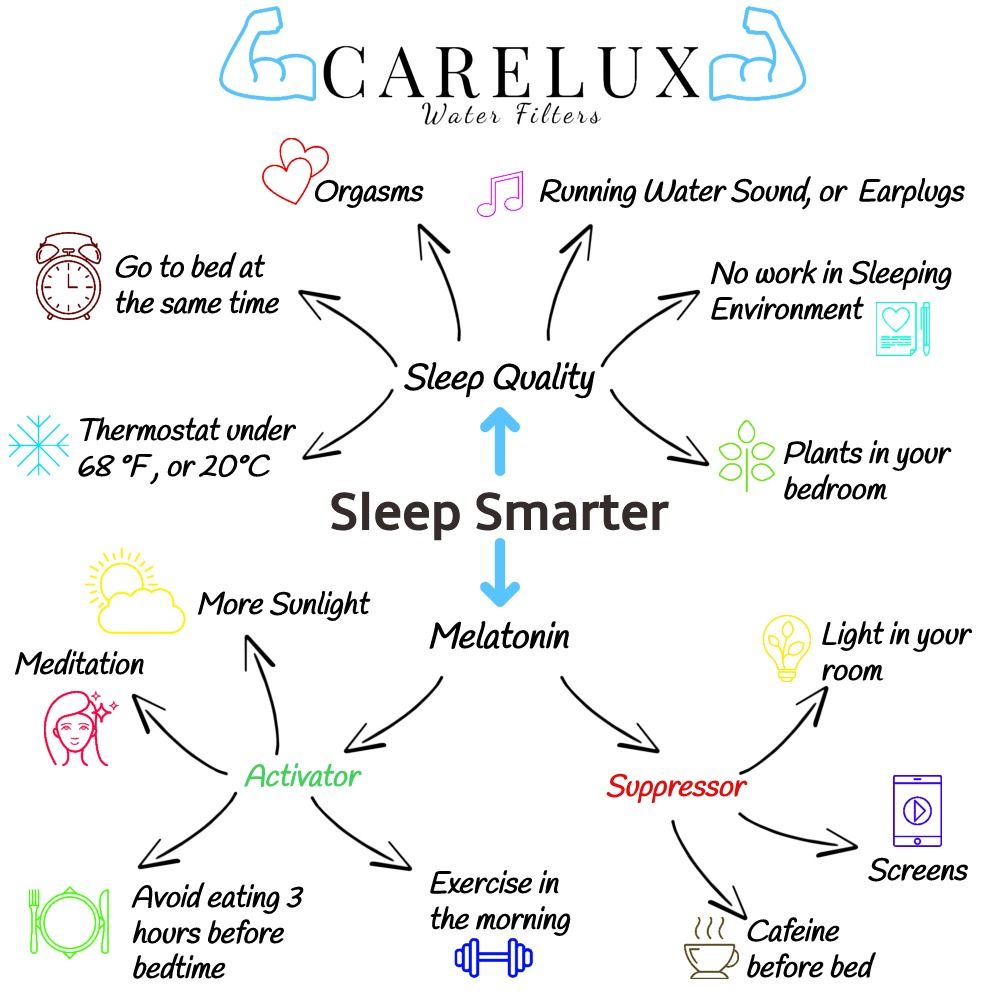
Exercise in the morning:
Body temperature starts to fall as bedtime approaches, paving the way for a good night’s sleep. Your body also tends to lose heat, which helps you fall and stay asleep. That’s one of the reasons experts say you shouldn’t exercise close to bedtime: Exercise heats you up. We sleep better when we’re cooler. Your temperature starts to rise toward morning, preparing your body for wakefulness.
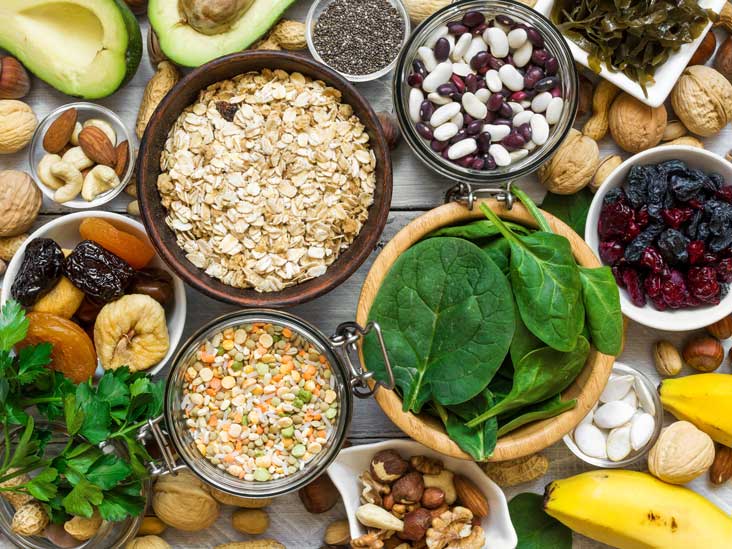

Magnesium:
Magnesium is a powerful mineral that is instrumental in sleep and is a natural relaxant that helps deactivate adrenaline. A lack of magnesium can be directly linked to difficulty going and staying asleep. Magnesium is often referred to as the sleep mineral. Excellent sources of magnesium are: Dark leafy greens (baby spinach, kale, collard greens), Nuts and seeds (almonds, sunflower seeds, brazil nuts, cashews, pine nuts, flaxseed, pecans), Soybeans, Banana, Avocados.
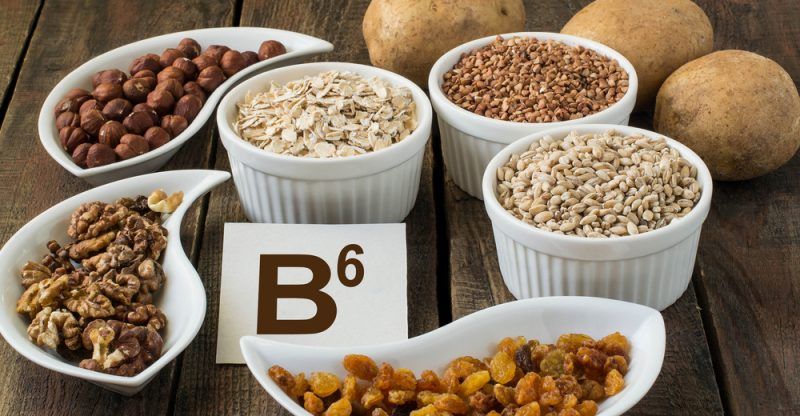

Vitamin B6
Vitamin B6 also helps convert tryptophan into melatonin. A deficiency in B6 has been linked with lowered serotonin levels and poor sleep. A deficiency in B6 is also linked to symptoms of depression and mood disorders which can lead to insomnia. Highest sources of B6 are: Sunflower seeds, Pistachio nuts, Flaxseed, Dried Prunes, Bananas, Avocado, Spinach.

Meditation:
The relaxation response can help ease many stress-related ailments, including depression, pain, and high blood pressure. For many people, sleep disorders are closely tied to stress. Mindfulness meditation involves focusing on your breathing and then bringing your mind’s attention to the present without drifting into concerns about the past or future.
It helps you break the train of your everyday thoughts to evoke the relaxation response, using whatever technique feels right to you.
More Sunlight:
A Finland study evaluated a two groups of rodents who were exposed to either natural sunlight or fluorescent light. One group received fluorescent lighting and the other group received natural sunlight.
Both groups experienced the same amount of daily sunlight, and both groups experienced the same amount of darkness throughout the night. After one week, the researchers measured the melatonin levels of the two groups and came up with a significant finding: The rodents that were given sun exposure produced FAR MORE melatonin at night than the ones in the artificially-lit room.

Reading:
Researchers at the University of Sussex found that half an hour of dedicated reading greatly reduces stress levels more than several other methods of relaxation, like listening to music or drinking tea. And since stress is a major factor in insomnia, reading can help you curb some of those negative thoughts swirling around in your brain before bed.

Keep your room dark, cool, and quiet
Most people sleep best in a slightly cool room (around 65° F or 18° C) with adequate ventilation. A bedroom that is too hot or too cold can interfere with quality sleep. Also, When it’s time to sleep, make sure the room is dark. Use heavy curtains or shades to block light from windows, or try a sleep mask. Also consider covering up electronics that emit light.
Shawn Stevenson
Sleep Smarter | Men’s Health
What inhibits melatonin production?
Lights
Turn out the lights. Darkness cues your body to release the natural sleep hormone melatonin, while light suppresses it. Curtains and shades on windows keep outside light from disturbing your sleep.
Bill Hendrik
Sleep Disorders| WebMD