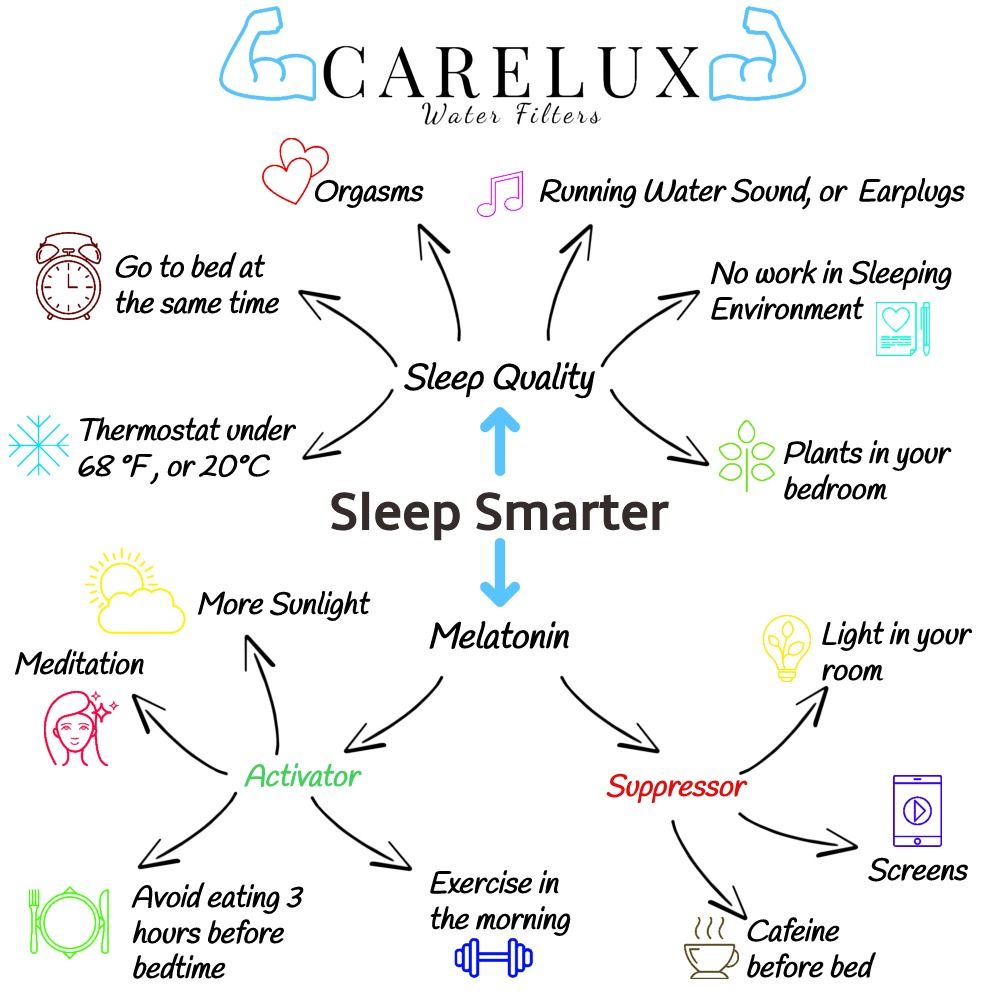
What inhibits melatonin production?
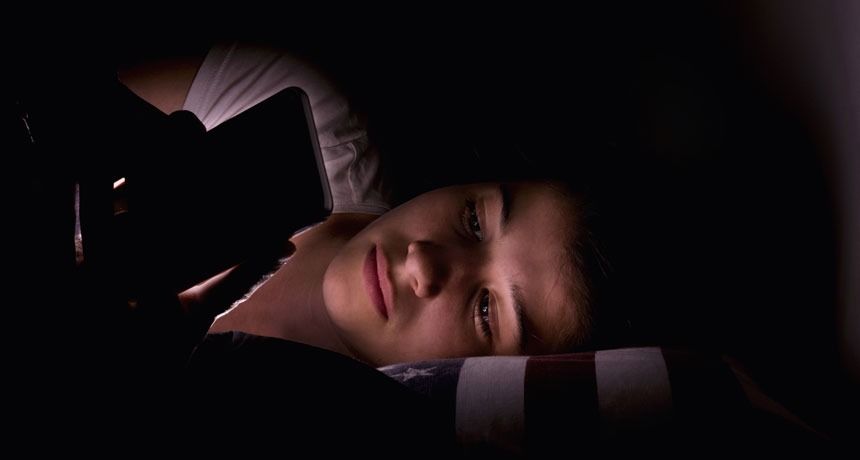




Light in your room:
Turn out the lights. Darkness cues your body to release the natural sleep hormone melatonin, while light suppresses it.
Curtains and shades on windows keep outside light from disturbing your sleep. Make sure window coverings are heavy enough to fully block light, and are well fitted to avoid slivers of streetlight or early morning sunlight from filtering in. Even brief exposure to light can interfere with sleep.

Blackout curtains are designed to provide this kind of thorough protection against unwanted light. If you need a source of light during the night—to make your way comfortably to the bathroom or to a child’s bedroom—use a nightlight with a red bulb.
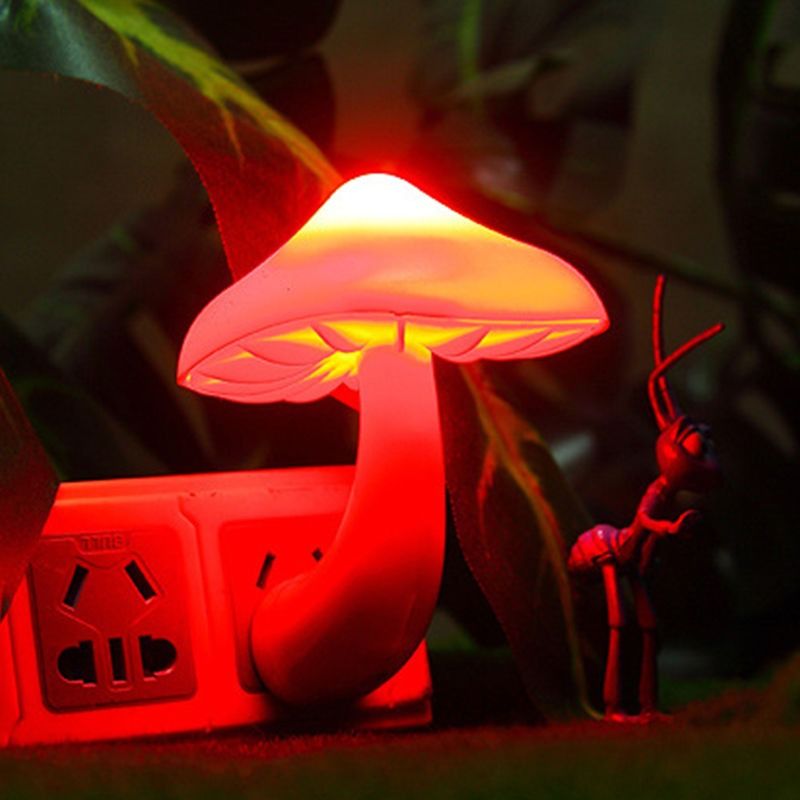


Keep your room dark, cool, and quiet
Most people sleep best in a slightly cool room (around 65° F or 18° C) with adequate ventilation. A bedroom that is too hot or too cold can interfere with quality sleep. Also, When it’s time to sleep, make sure the room is dark. Use heavy curtains or shades to block light from windows, or try a sleep mask. Also consider covering up electronics that emit light.
Shawn Stevenson
Sleep Smarter | Men’s Health
Activate Melatonin Production in your Body
Increase Melatonin levels in your body with exercise in the morning. Body temperature starts to fall as bedtime approaches, paving the way for a good night’s sleep. Your body also tends to lose heat, which helps you fall and stay asleep. That’s one of the reasons experts say you shouldn’t exercise close to bedtime: Exercise heats you up. We sleep better when we’re cooler. Your temperature starts to rise toward morning, preparing your body for wakefulness.
Melinda Smith
Sleep Medicine | Harvard Medical School