How to Sleep Better: Benefits of Sleep
1. Earplugs:
Sleeping with earplugs can significantly increase the quality of your sleep. For many people, earplugs are the only way to block out sounds while they sleep, such as noise from a nearby freeway or a snoring partner.
This is significant because the quality of your sleep matters just as much as the amount you get. Loud sounds can wake you up out of a deep sleep. This has lasting effects, even if you wake up only for a few seconds. It takes time for your body to return to that phase of deep sleep that your body needs after a full day.
“Lack of sleep causes leptin levels within the body to plummet, signalling your brain to eat more food or to continue eating when you should have stopped.”

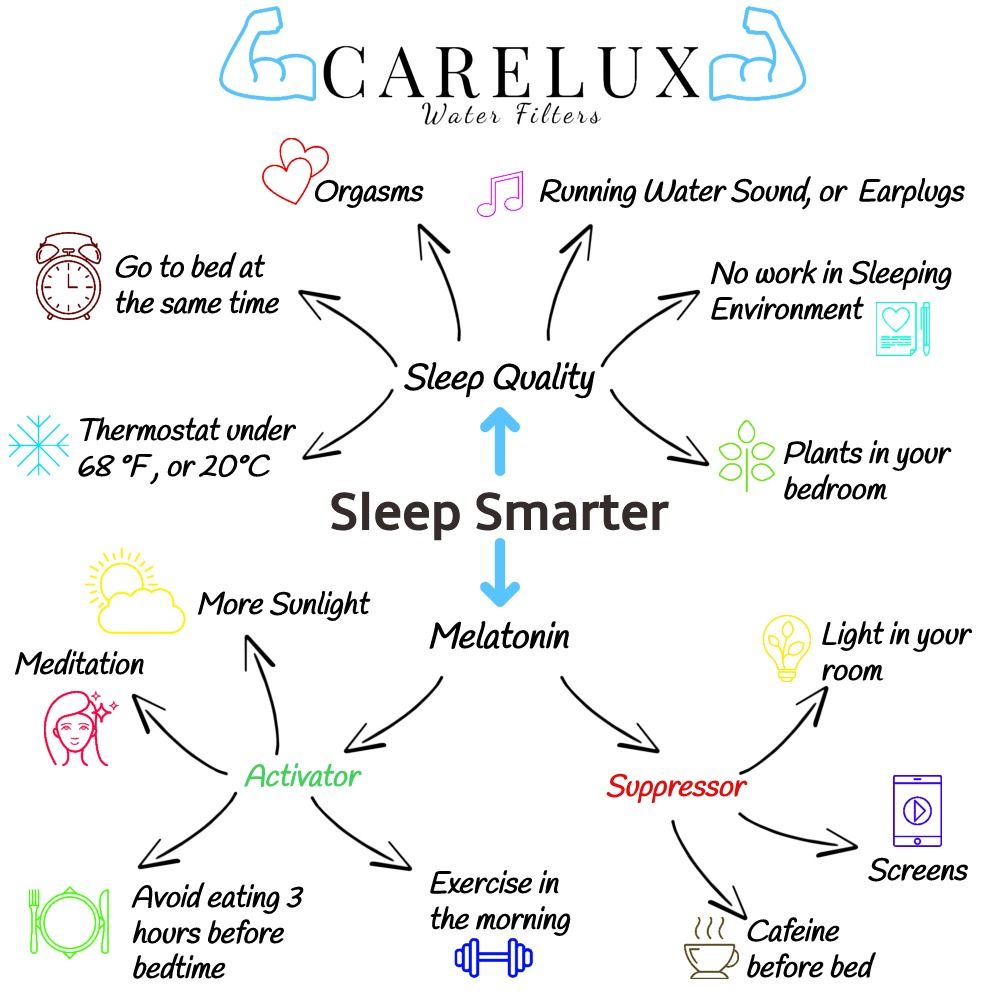
2. Go to bed at the same time:
Go to bed at the same time each night, ideally, even on weekends—this helps regulate your body clock. Put your phone in another room, purchase an alarm clock.
Scientists who work in sleep health have a term for the period of time it takes you to get to sleep: it’s called your sleep latency. And it turns out that maintaining a regular sleep schedule, according to several small studies, may cut down on the amount of time you spend tossing and turning before drifting off.
“In our experiment, sleep restriction was accompanied by a similar pattern of increased hunger and … reduced oxidation of fat.“

“However with poor sleep insulin sensitivity can drop by more than 30 percent. If your body doesn’t respond properly to insulin then it has trouble processing fats from your bloodstream and consequently stores them as fat.“
3. Thermostat under 20C:
The role of temperature has gained attention since a study published last year found that core body temperature, which tends to fluctuate by a few degrees over the course of the day, needs to drop to help initiate sleep.
Setting the thermostat to around 18C is good for sleep, studies have found. Research has also found that room temperatures as low as 16C are best when people pile on the blankets.
Continuing along that same vein, keeping your sleeping environment below 70 degrees (F) every night can help your body regulate its melatonin and growth hormone levels. These chemicals help the body do things like prevent aging and are essential to good health.
“Getting enough sleep can help to protect your mental health, physical health, quality of life and overall safety.“
4. Orgasms:
When you orgasm, you release a cocktail of hormones that actually promote good sleep. Oxytocin ― a.k.a. the love hormone ― counteracts stress hormones, which helps you fall asleep. And serotonin and norepinephrine help the body cycle through REM and deep non-REM sleep cycles.
“Sleep not only makes you feel better but adequate sleep is a key part of a healthy lifestyle, as during your sleeping hours your body is working to support healthy brain function and physical health.“

5. Plants in your Bedroom:
One way to ensure a better quality of sleep is to fill your home with beautiful flowers and plants. Not only do they look great and bring vitality and life to your living spaces, but they can have fantastic relaxing and purifying benefits – which in turn can promote a healthy sleeping pattern.
Jasmine, Lavender, Snake Plant, Aloe Vera, Gardenia, Spider Plant, Valerian, Englush Ivy, Peace Lily, Golden Photos, Gerbera Daisies, Bamboo Palm.
“Getting adequate sleep also helped control the dieters’ hunger. Average levels of ghrelin did not change when dieters spent 8.5 hours in bed. When they spent 5.5 hours in bed, their ghrelin levels rose over two weeks from 75 ng/L to 84 ng/L.“

6. Runing Water Sound:
Classical music and nature sounds affect levels of cortisol and alpha-amylase.The alpha-amylase levels of people who listened to classical music went back to normal more quickly compared to the people listening to nature sounds. This suggests that relaxing music helps the body to return to a non-stressed state more quickly.
The people listening to relaxing music shows a stress response that is shorter compared to the other groups. The shorter response helps to prevent the body from getting worn out. This means that listening to relaxing music might help to improve the stress response and health
“So sleeping more won’t make you lose weight, but not getting enough sleep will certainly hamper your metabolism and lead to weight gain.“

7. No Work in Sleeping Environment:
Remove the electronic and other distractions from the environment. Go to your bedroom when it is time to go to sleep, and avoid doing other activities.
This will set up a psychological connection in your head between getting in bed and going to sleep. Create a bedtime ritual. It’s not the time to tackle big issues. Instead, take a warm bath, meditate, or read.
“Higher ghrelin levels have been shown to reduce energy expenditure, stimulate hunger and food intake, promote retention of fat, and increase hepatic glucose production to support the availability of fuel to glucose dependent tissues“

“Too little sleep triggers a cortisol spike. This stress hormone signals your body to conserve energy to fuel your waking hours.“
8. Sleep Naked:
Helps you regulate your cortisol. When you sleep naked, it helps keep your body temperature at the optimal ranges so your body can better create cortisol. If you sleep overheated your cortisol levels tend to stay high, even after you wake up.
This can lead to increased anxiety, cravings for bad food, weight gain, and more terrible things. Sleep naked so you can keep your body temperature down and sleep well so your body can properly produce and regulate cortisol. Also, balances your melatonin and growth hormone.
When you sleep in clothes, your body heats up and prevents effective use of these hormones. In other words, sleeping with clothes on makes you grow old faster.
“The body’s core temperature needs to drop by about two to three degrees to initiate sleep.”

9. Night Mask:
An eye mask worn at night can help deepen darkness and protect against intrusive light. Choose a mask that is soft, comfortable, and flexible. Wearing an eye mask can take a little getting used to, but it is a highly effective tool for limiting your light exposure at night.
“Your brain also operates differently when it’s tired, it dulls the activity in the brain’s frontal lobe which focuses on decision making and impulse control.“

Benefits of Good Sleep
- Boosts Your Academic Performance
- Makes You Happier
- Protects You From Cardiovascular Disease
- Better For Your Metabolism
- Improve Concentration and Productivity
- Maximize Athletic Performance
- Improves Your Immune Function
Researchers found that when dieters cut back on sleep over a 14-day period, the amount of weight they lost from fat dropped by 55%, even though their calories stayed equal. They felt hungrier and less satisfied after meals, and their energy was zapped.
Shawn Stevenson
Sleep Smarter | Men’s Health

Activate Melatonin Production in your Body
Increase Melatonin levels in your body with exercise in the morning. Body temperature starts to fall as bedtime approaches, paving the way for a good night’s sleep. Your body also tends to lose heat, which helps you fall and stay asleep. That’s one of the reasons experts say you shouldn’t exercise close to bedtime: Exercise heats you up. We sleep better when we’re cooler. Your temperature starts to rise toward morning, preparing your body for wakefulness.
Melinda Smith
Sleep Medicine | Harvard Medical School
What inhibits melatonin production?
Lights
Turn out the lights. Darkness cues your body to release the natural sleep hormone melatonin, while light suppresses it. Curtains and shades on windows keep outside light from disturbing your sleep.
Bill Hendrik
Sleep Disorders| WebMD