Fenugreek
What are the benefits of Fenugreek?
Fenugreek is mostly used for diabetes, painful menstruation, menopause, polycystic ovary syndrome, arthritis, poor thyroid function, and obesity. It is also used for conditions that affect heart health such as “hardening of the arteries” (atherosclerosis) and for high blood levels of certain fats including cholesterol and triglycerides.
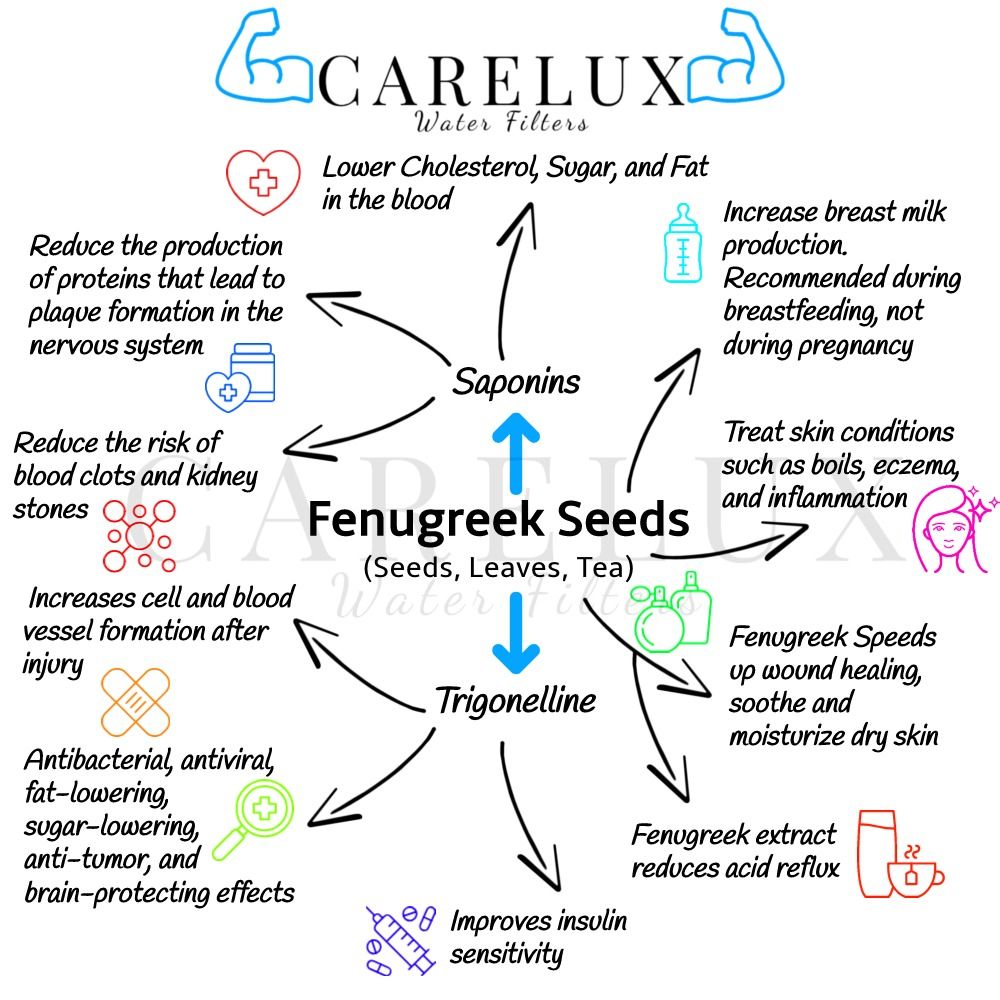
The seeds of fenugreek have long been known as a traditional medicine, having hypocholesterolemic and antidiabetic effects, and other active compounds. The hypocholesterolemic activity is related to the defatted part of the seed extract and involves saponin-rich subfractions, such as;
- Saponins: help protect against cancers and lower cholesterol, sugar, and fat in the blood. Saponins can also reduce the risk of blood clots and kidney stones.
- Trigonelline: It has antibacterial, antiviral, fat-lowering, sugar-lowering, anti-tumor, and brain-protecting effects.
However, these structurally diverse compounds have also been observed to kill protozoans and molluscs, to be antioxidants, to impair the digestion of protein and the uptake of vitamins and minerals in the gut, to cause hypoglycaemia, and to act as antifungal and antiviral agents.

| Benefits
- Control Diabetes and Blood Sugar Levels
- For digestion, and appetite control
- Anti-inflammatory effects
- Reduce pain in women with painful menstrual periods
- Fenugreek is used for kidney ailments, a vitamin deficiency disease called beriberi, mouth ulcers, boils, bronchitis, infection of the tissues beneath the surface of the skin (cellulitis), tuberculosis, chronic coughs, chapped lips, baldness, cancer, Parkinson’s disease, and exercise performance.
- Some men use fenugreek for hernia, erectile dysfunction (ED), male infertility, and other male problems. Both men and women use fenugreek to improve sexual interest.
- Contains many compounds with antioxidant activity. These include apigenin, luteolin, caffeic acid, and coumaric acid.
- Fenugreek oil contains a high concentration of polyunsaturated fats (approximately 84%). This helps increase cell and blood vessel formation after injury.
| Contradictions
- People who are allergic to chickpeas may also have adverse reactions to fenugreek because the two plants contain similar proteins and allergens.
- Fenugreek can cause hyperthyroidism (in rats), so people with thyroid problems should avoid fenugreek.
- Since fenugreek affects uterine contractions, it should not be taken during pregnancy, but it is safe afterward during breastfeeding.