Can Coeliac Disease be cured naturally?
Major causes: Gluten
What goes wrong?
People allergic to gluten are also susceptible to damage to the lining of the small intestine. Normally, food passes through the stomach into the small intestine, where the food is digested and absorbed, and then passed to the large intestine as waste mater. This material is finally forced as faeces (bowel movement) through the anus.
The small intestine is lined with billions of minute fingers called villi, which increase the area of the walls of the intestine, so that nutrient absorption is more efficient. By consuming gluten via wheat products, the villi are flattened down and pasted together. The natural absorption of nutrients is blocked, and in many cases, you are not feeding the body, regardless of what volumes of food you eat.
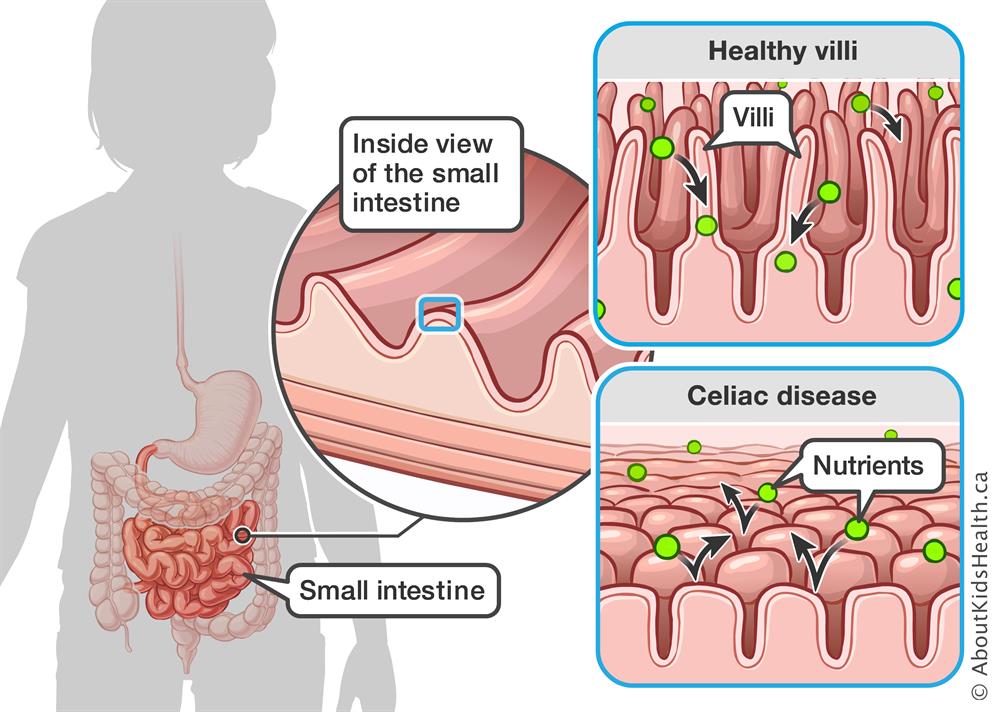
From: aboutkidshealth.ca
| Offensive smell
At the same time, some unabsorbed food passes into the large intestine and out in the bowel motions. This food os often fermented and putrefied by unfriendly bacteria living in the large intestine, and produces and offensive smell and lots of wind. The most obvious symptoms are foul-smelling faeces and bloated abdomen.
Coeliac can produce diarrhoea, irritability and pot belly, as well as poor weight and growth. Weight-loss is often evident around the buttocks and legs. The lack of nutrient up-take causes vitamin and mineral deficiencies which can lead to anaemia. If one needs a medical diagnosis, a gastroenterologist should be consulted Usually, a biopsy will determine if villi are incapacitated.
| Who is a likely to Coeliac Suferer?
Many infants are born with a predisposition to this dangerous condition. Some races have a particularly high incidence of coeliac, due to their cultural eating habits, which include an abundance of wheat, bread, rye, barley, oats and triticale. However, anyone may suffer some degree of coeliac. It may be genetically-based disease, because of the same eating habits passed down from mother to daughter, generation after generation.
Coeliac and Cancer
There appears to be an increased risk of cancer of the small intestine in untreated coeliac disease. Symptoms may develop early in infancy after the introduction of bread with gluten into the diet, or at any time in years or decades to come. A gluten-free diet must be maintained for a long healthy life.
Treatment
Any gluten will cause some damage, which becomes progressively worse with repeated exposure. Fortunately, the reverse is also true. Removal of gluten from the diet allows the lining of the intestine to return to normal in a few weeks. Put simply: all gluten based grains such as wheat, rye, oats, and products made from them, should be avoided.
To aid the healing process, it is important to take some fibre in the form of celery, raw vegetables and fruit. A good combination is raw bran mixed with acidophilus and bifidobacterium added to yogurt. Other ingredients could be added, if desired, such as ground flaxseed, lecithin granules, rice polishing and psyllium husks. It is also advisable to increase the hydrochloric acid in your stomach for better digestion, by drinking a glass of filtered water 15 minutes before you eat a meal, as well as to take digestive enzyme tablets. This will help your reduce and eliminate the excess wind.
Although a gluten-free diet is difficult to maintain. It is the best way to avoid this painful ailment. Maintaining a gluten-free diet is so rewarding that it truly makes you feel a new person, both physically and mentally.
Things to avoid

- All wheat, rye, barley, oats, malts, and triticale products, and all breads and buns, cakes, pastries, muffins. They contain gluten and must be totally avoided.
- Crumbed and battered foods, frankfurts, sausages, bacon, hot dogs pies, pizza, sandwiches, sausage rolls.
- Alcohol, canned soups, coffee, msg, packet soups, porridge.
Essential Foods
Capsicum, garlic, ginger, carrot, parsnip turnip, spinach, green sprouts, shallot, cucumber, parsley, potato, pumpkin, kohlrabi, celeriac root, leeks, chives, celery, cabbage, green beans, string beans, sweet potato, tomato, onion, watercress, lettuce, choke, Chinese vegetables, Brussels sprouts, broccoli.